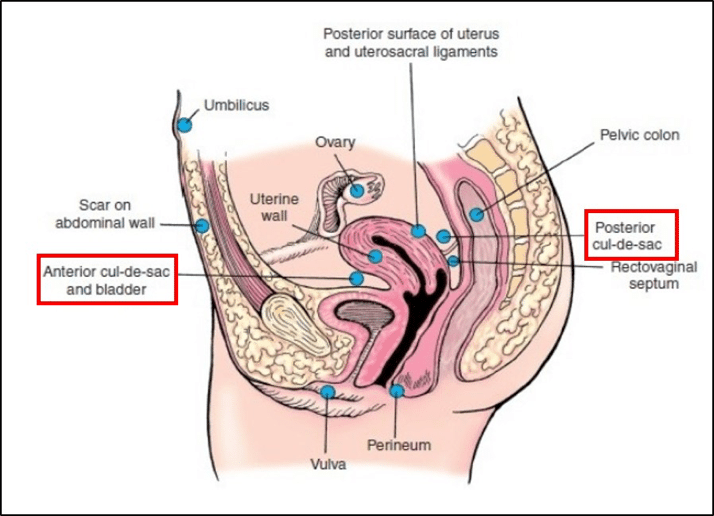
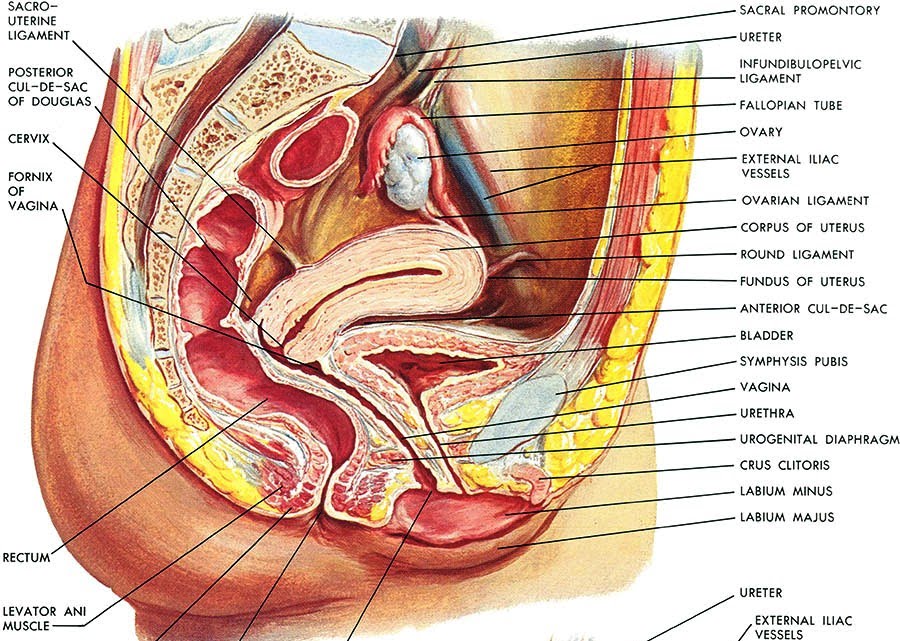
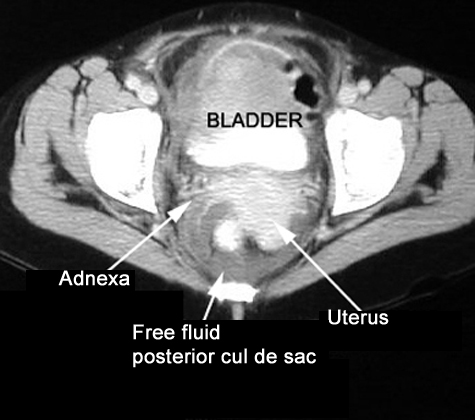
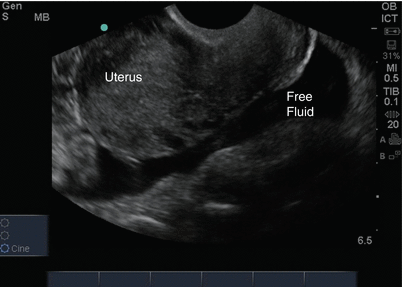
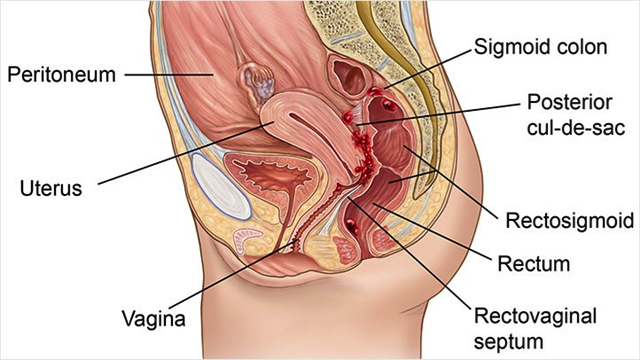
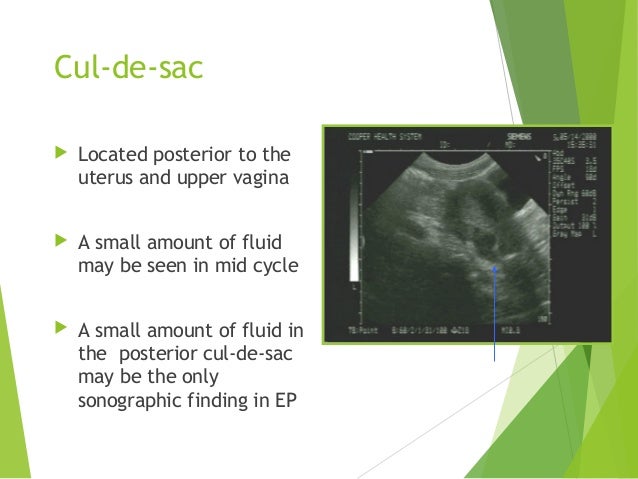
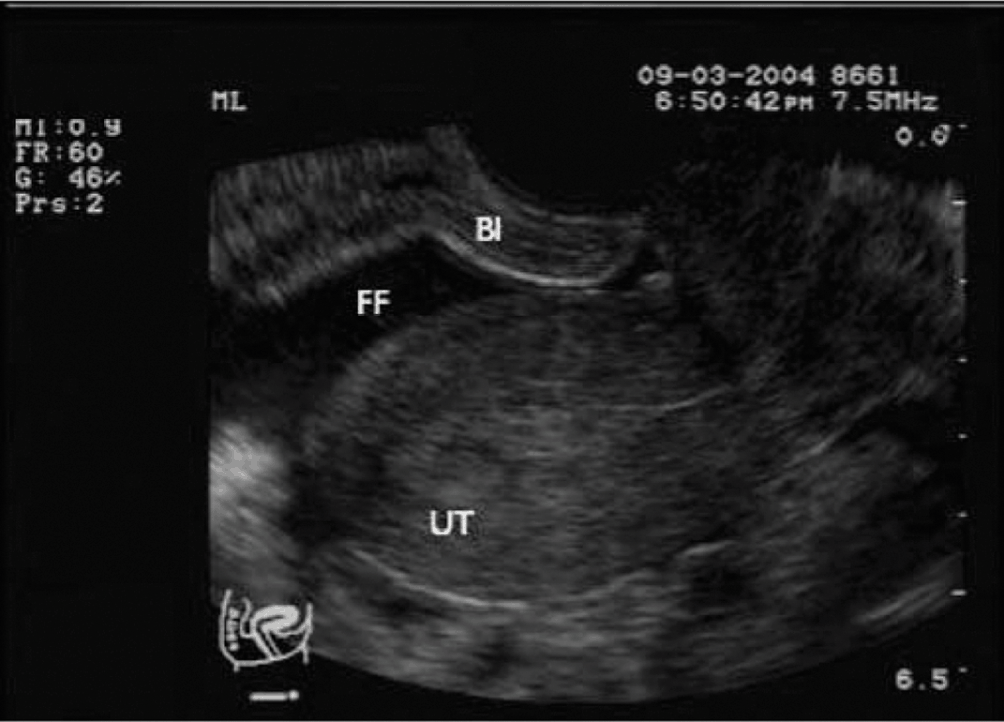
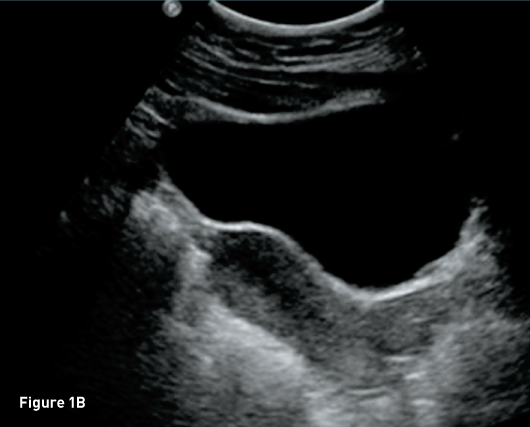
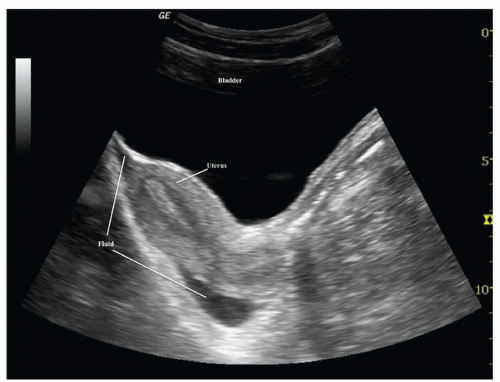
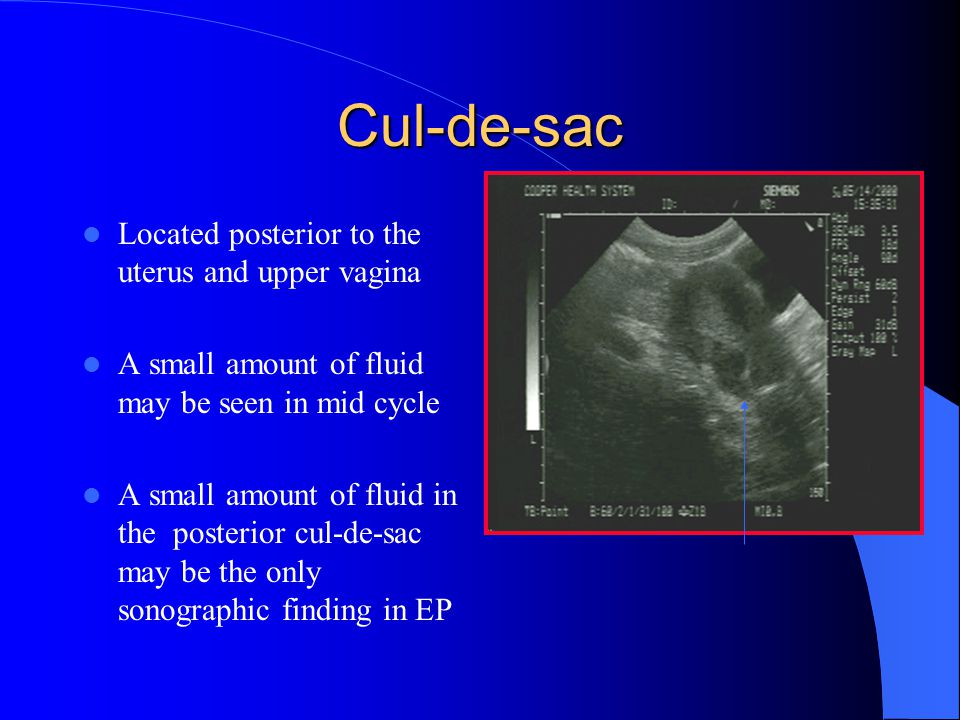
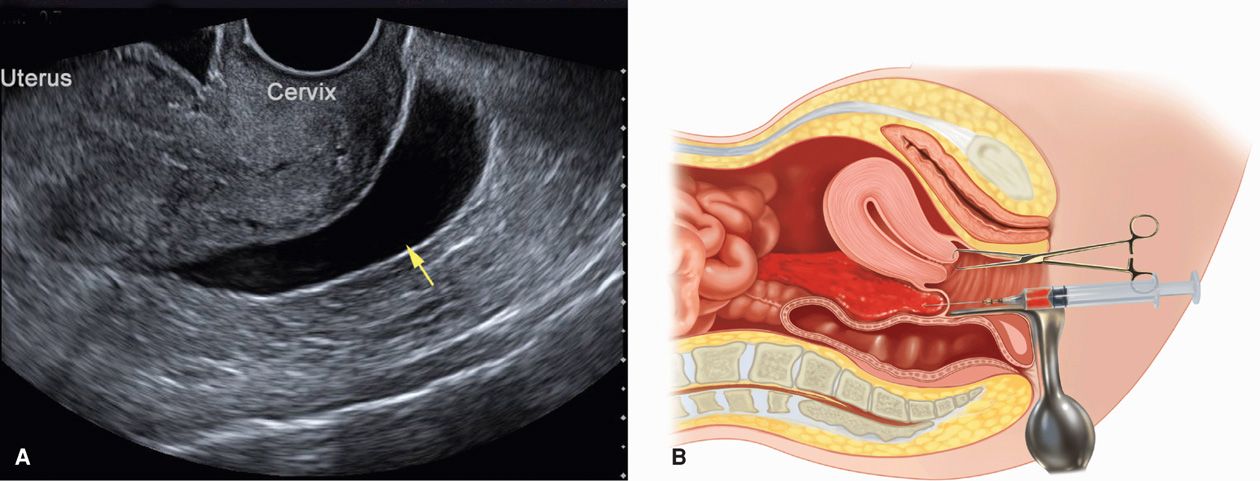
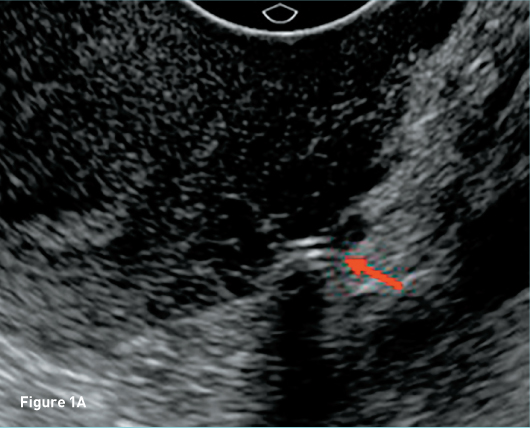
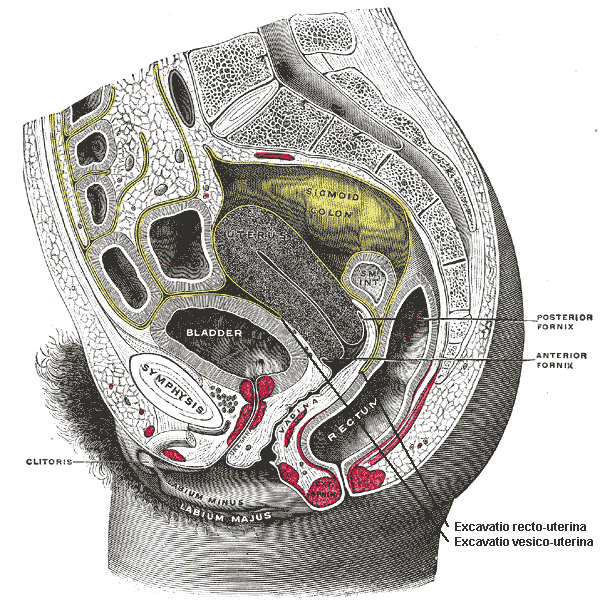
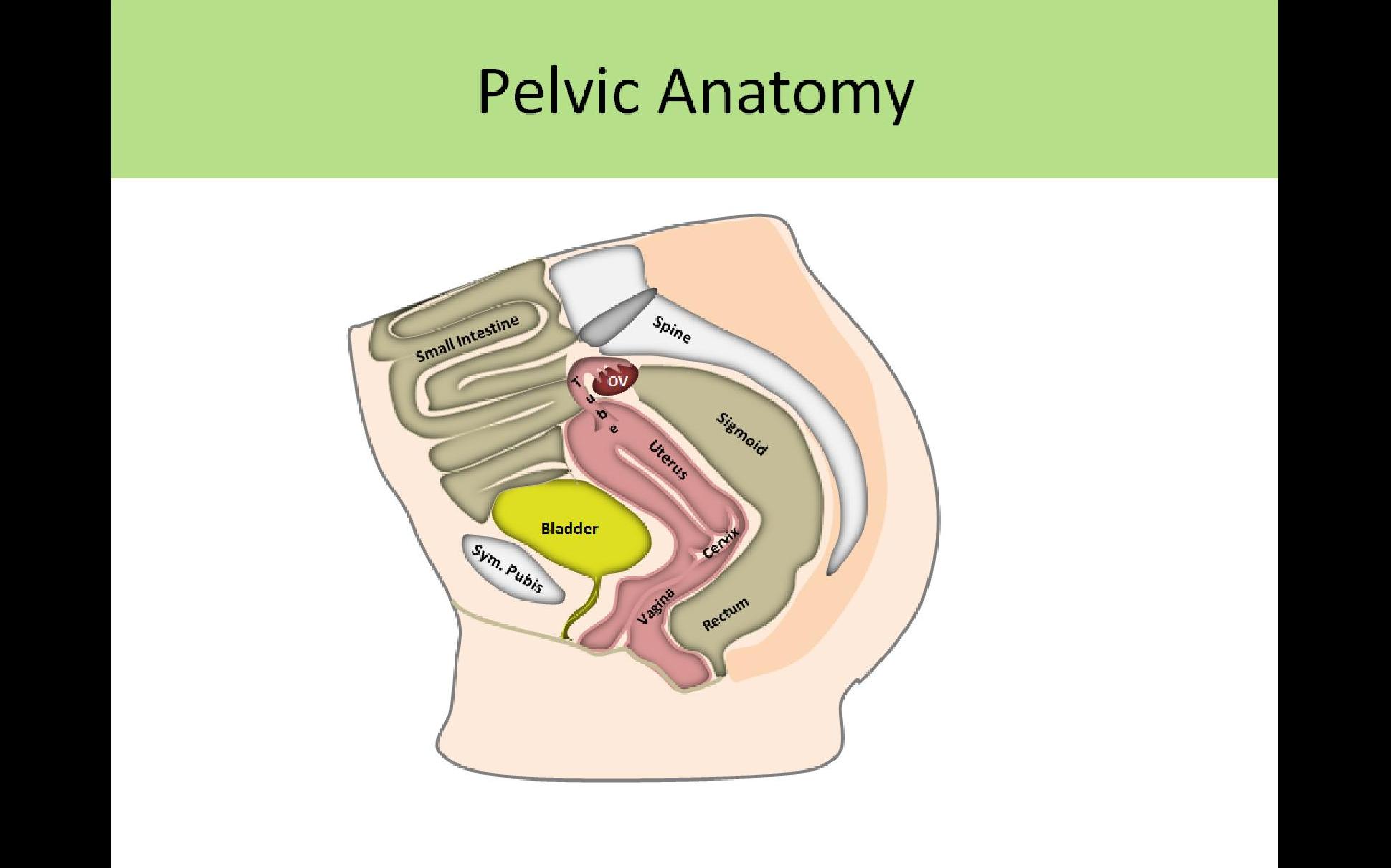
Female Cul De Sac Fluid

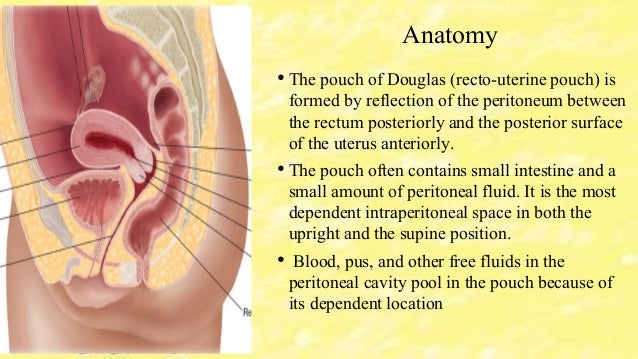
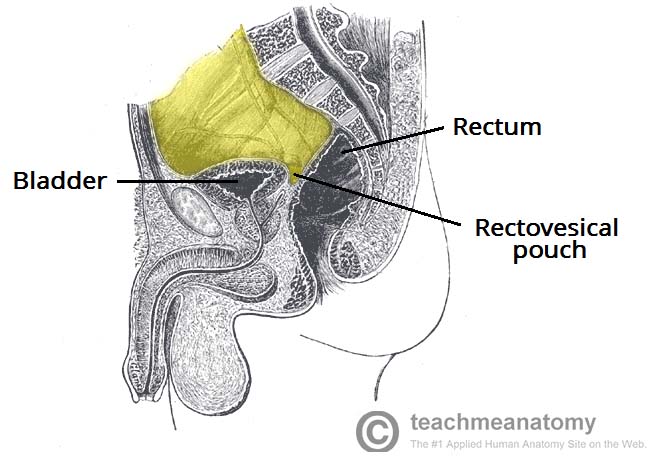
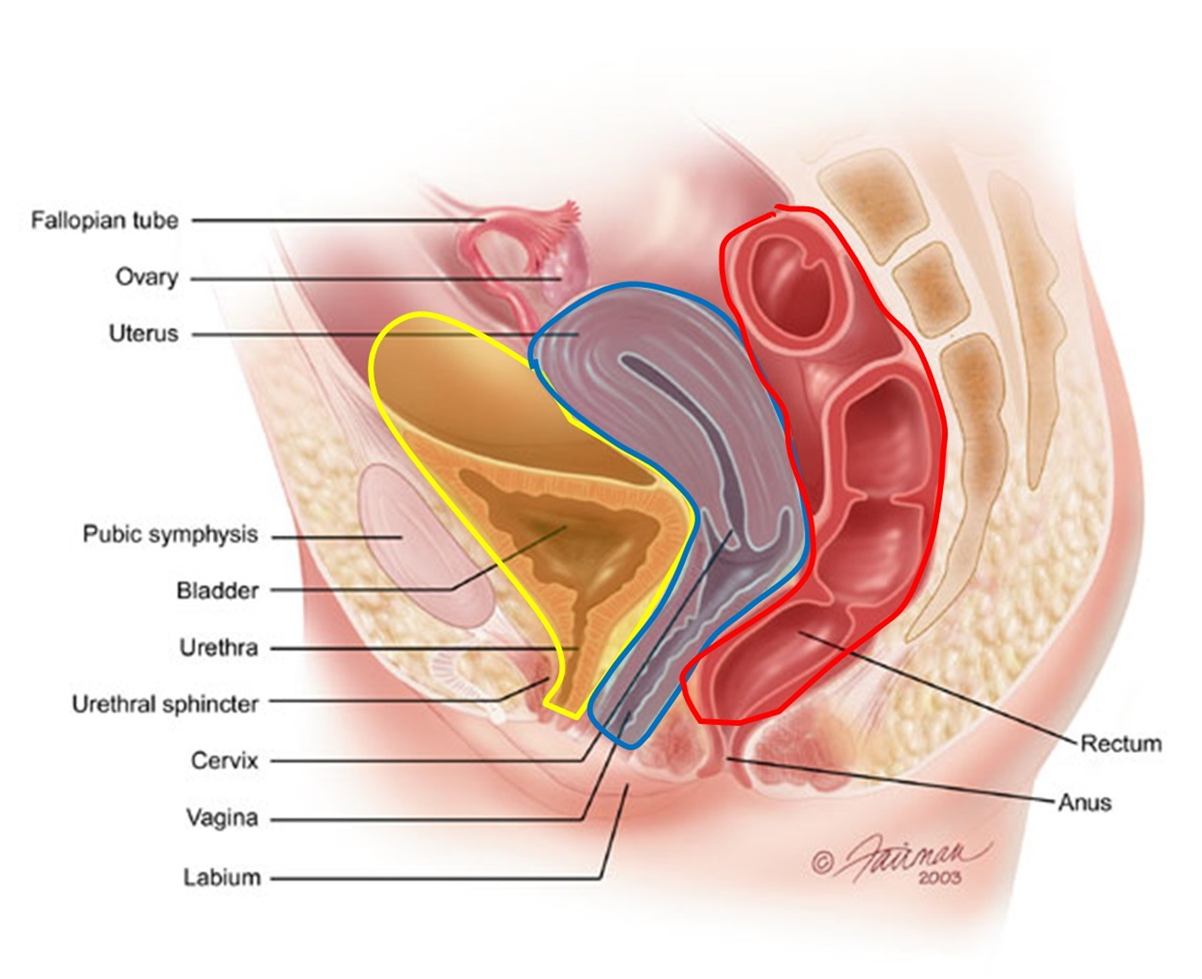
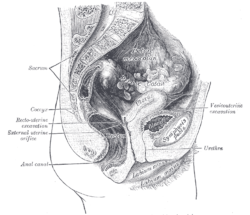
In women it is the deepest point of the peritoneal cavity posterior to behind the uterus and anterior to in front of the rectum.
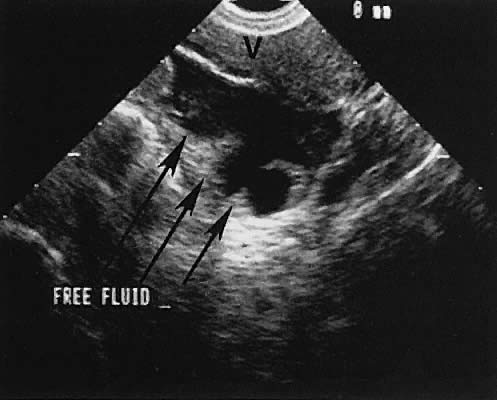
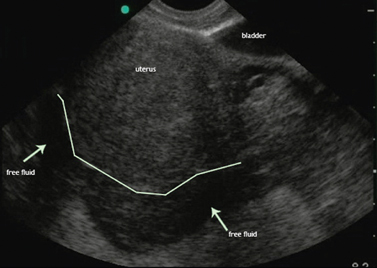
Female cul de sac fluid. Most women have small amount of fluid in the cul de sac and you dont need to worry about it. Cul de sac fluid is a common ultrasound finding in women of reproductive age and can be a normal finding or suggest a problem that needs to be investigated based on the context. Increase in ovarian permeability due to estrogen influence.
If no signs of abscess or appendicitis then in can come from a rupture ova. Fluid in cul de sac. Physiological pelvic intraperitoneal fluid in women may be due to.
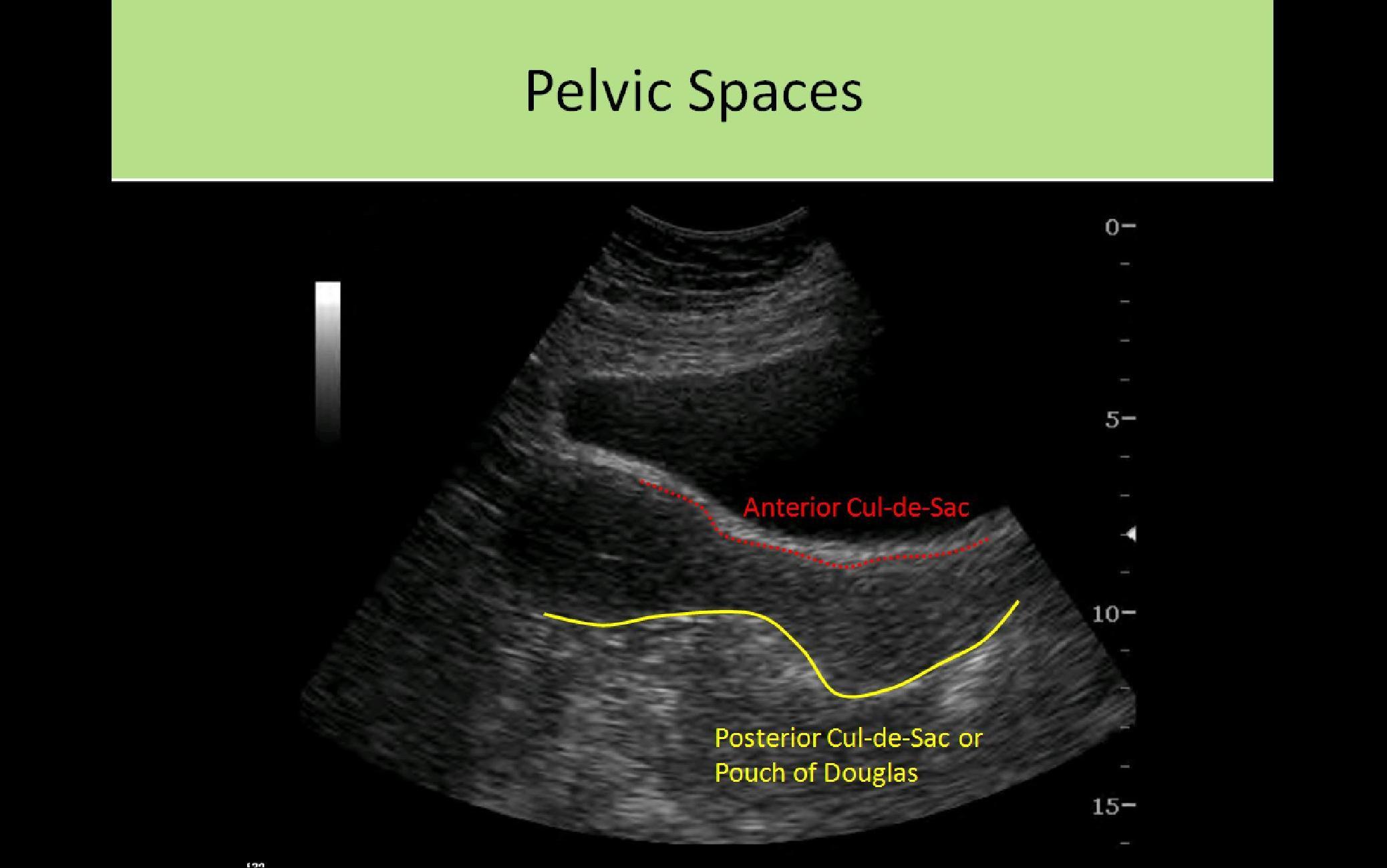
The female pelvis is a complex and ever changing area of the human body and the pouch of douglas is a particular area of contrasts. The pouch on the other side of the uterus is the vesico uterine pouch it is near the posterior fornix of the vagina. Physiologic and pathologic cul de sac fluid takes many forms.
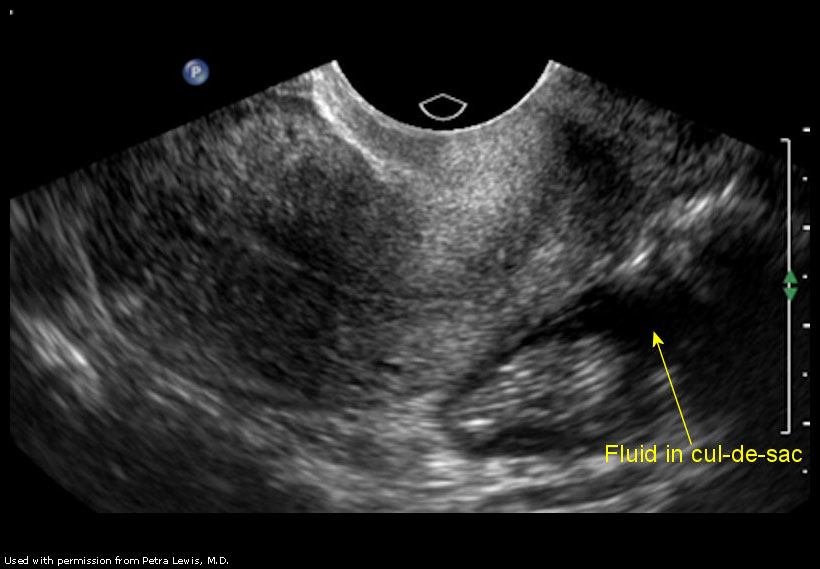
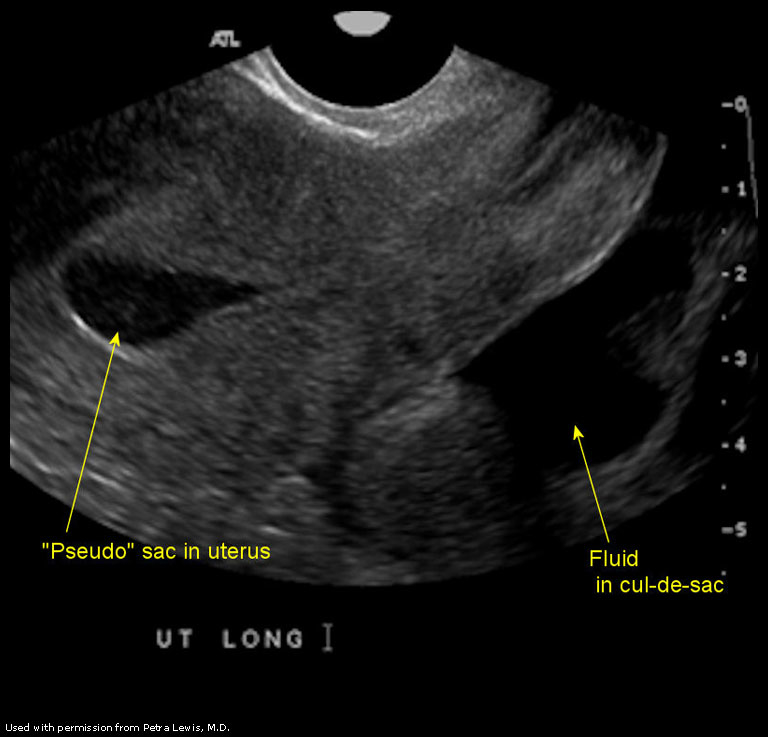
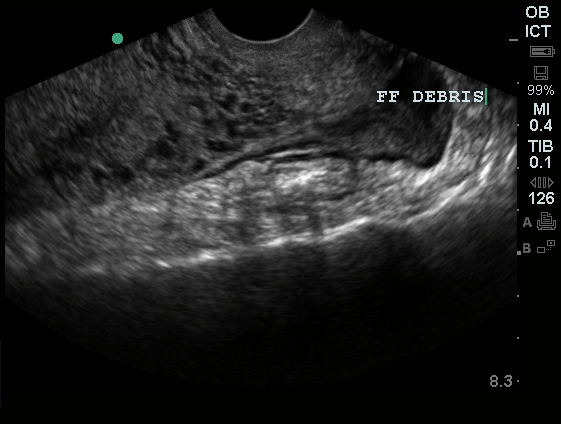
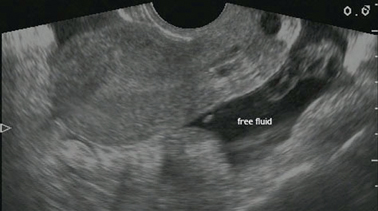
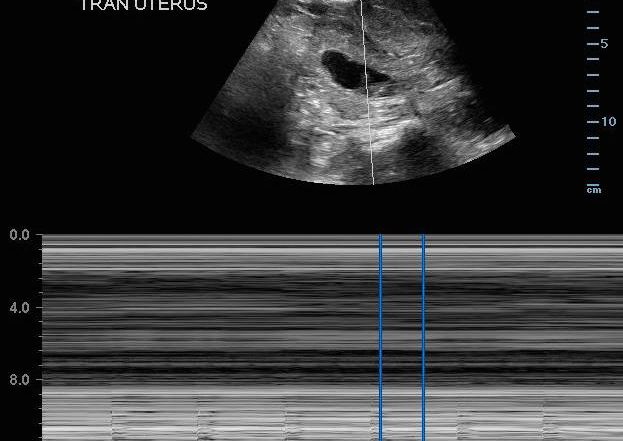
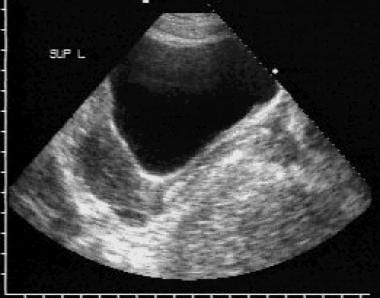
Also known as the cul de sac the pouch of douglas exists between the uterus and the rectum and is the most dependent area of the pelvis where fluids pool. This is often seen when doing an ultrasound for abdominal pain in females. Talk to your doctor.
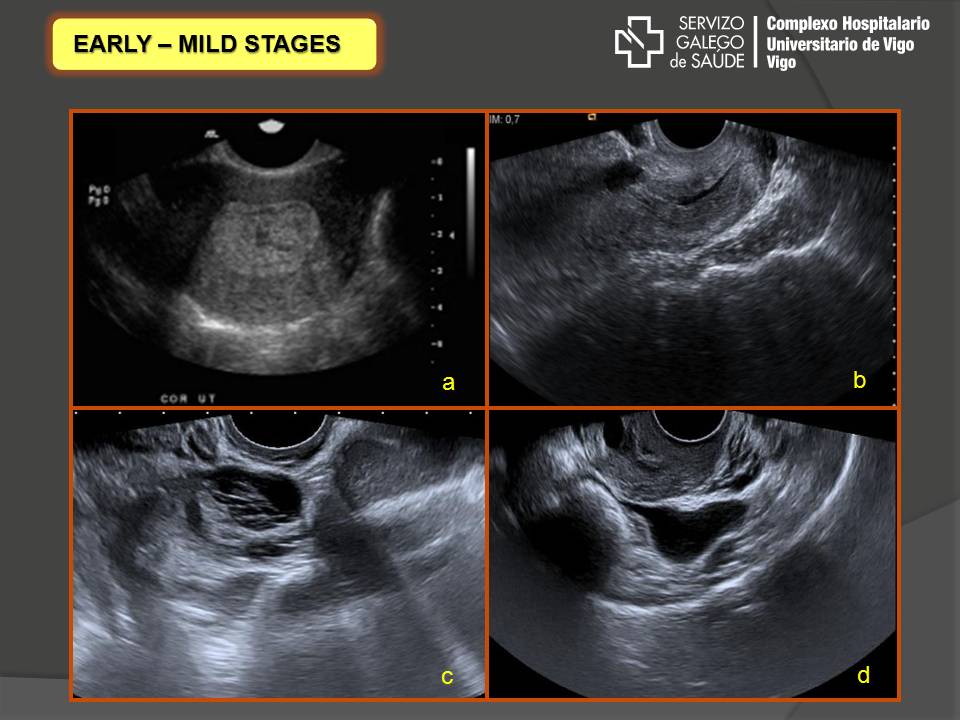
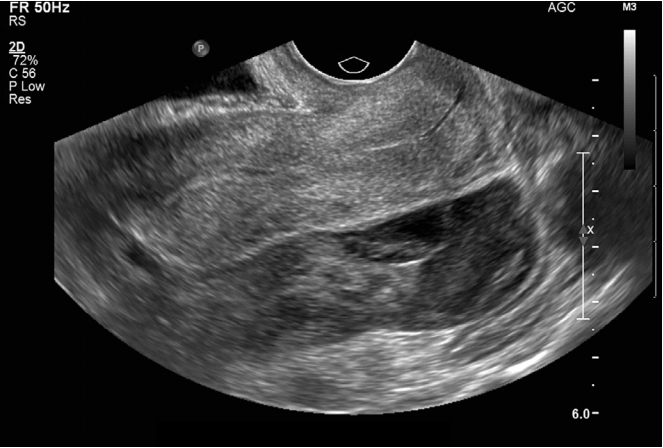
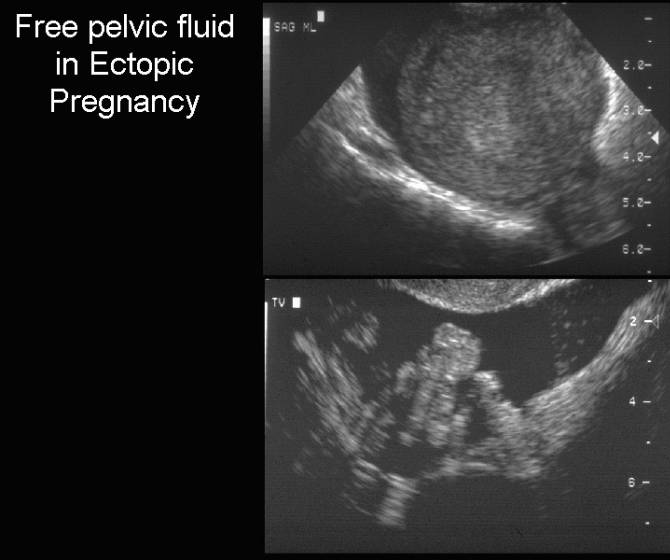
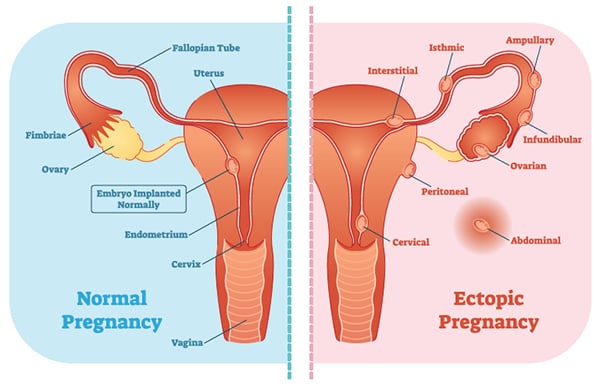
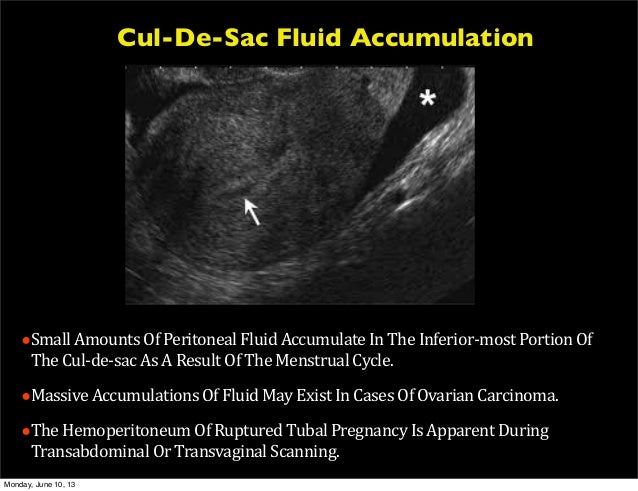
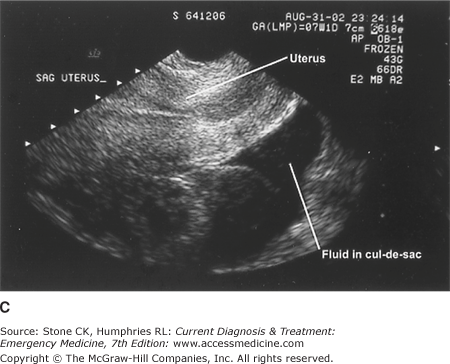
It is normal to have approximately 1 to 3 ml or ml of fluid in the recto uterine pouch throughout the menstrual cycle. In some cases excessive cul de sac fluid is a sign of an acute problem that needs to be addressed including a ruptured ovarian cyst ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome ohss or ectopic pregnancy. In women undergoing fertility treatment fluid in the cul de sac as seen on ultrasound is a common finding in ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome ohss.
The anterior cul de sac is the space between your bladde. Having the colonoscopy because i was suppose to have one every 5 years and im a year behind. Cul de sac fluid normally accumulates after a follicle has ruptured and indicates a woman has ovulated.
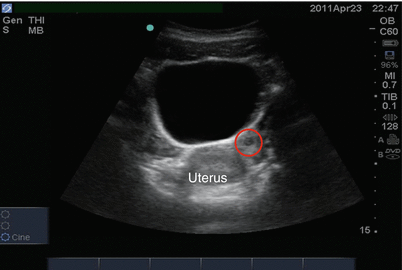
As far as my report like i mentioned it said that the right and left ovary was unremarkable and the uterus was unremarkable and that there was a small amount of fluid in the posterior cul de sac. Presence of fluid within the cul de sac is a common finding and the underlying cause can be thought of as either physiological or pathological.



















































/pregnancy-ultrasound-scan-478187269-5be1cc1546e0fb00515a903b.jpg)